This is an old revision of the document!
Myanmar
Brief About Myanmar
The Republic of the Union of Myanmar, commonly shortened to Myanmar.
Geography
- The total land area of 676,577 square kilometre
- International borders of 5858 Kilometer with Bangladesh, India, China, Thailand and Laos
- total coastal line length 2832kilometer
- 2090 kilometre (north to south )and 925 kilometres (east to west )
Topography
- 50% of mountains and forests (northern and eastern)
Population
- Over 51.49 million Population
- 135 ethnic groups
- Seven states and seven Regions
- 70% of the population lived in rural areas and occupied in agriculture sectors
Natural Resources
- Rice, minerals, teak, hardwood forest, onshore and offshore oil fields, and precious stones such as rubies, jade sapphires, and pearls with the highest quality
Telecommunications Sector Reform
Policy Reform
- The Myanmar Telegraph Act 1885, The Myanmar Wireless Telegraph Act 1934 –> Telecommunications Law 2013
- Telecommunication Service License (Chapter III of Telecommunication Law) –> Anyone who is willing to provide telecommunications facilities and/or telecommunication services shall apply for permission and license
Key Objectives of Licensing Regime
- Promote competition and liberalization of the telecom sector in Myanmar
- Ensure transparency in market entrance
- Establish technology-and-service neutral approach to licensing
- Ensure non-discriminatory treatment of similarly situated licensees
Laws and Regulations
| Sr. No | Name | Issued Date |
| 1. | Telecommunication Law | 8-10-2013 |
| 2. | Licensing Rules | 14-10-2014 |
| 3. | Interconnection Rules | 6-1-2015 |
| 4. | Competition Rules | 9-6-2015 |
| 5. | Numbering Rules | 3-12-2015 |
| 6. | Spectrum Rules | 7-3-2015 |
Licensing Framework Multi-service licensing framework ° to simplify licensing
Processes ° encourage entry and expansion of services and ° increase End-User access to Telecommunications Networks and Telecommunications Services.
License Type NFS (I) NS AS NFS (C)
Maximum of two Telecommunications Service Licenses NFS (C) + NS OR AS
Licensing Category
NFS license (not exhaustive)
- Terrestrial fixed-line and radio transmission
- Submarine cable facilities
- Satellite earth station facilities
- Mobile base station facilities and passive infrastructure to deploy networks
NS license (not exhaustive)
- Wireline connectivity services
- Terrestrial wireless connectivity services
- Satellite uplink/downlink connectivity services
- International and domestic network transport and switching services
- International gateway services
AS license (not exhaustive)
- Public payphone services
- Public switched data services
- Audio text hosting services provided on an opt-in basis
- Directory services
- Internet service provider services
- Messaging services and Value-added services
NFS(C) (not exhaustive)
- Towers, masts, ducts
- Trenches and poles
- Dark fibre
Type of License and Licensees
| Sr. | Type of License | Number of Licensees | ||
| 1. | Nationwide Telecommunications License | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| 2. | Network Facilities Service (Individual) License (NFS-I) | 35 | 11 | 46 |
| 3. | Network Facilities Service (Class) License (NFS-C) | 25 | 16 | 41 |
| 4. | Application Service License ( AS ) | 17 | 4 | 21 |
| 5. | Network Service License ( NS) | 9 | 6 | 15 |
| Total | 88 | 39 | 127 |
National Policy
Myanmar Telecommunications Masterplan
The Myanmar Telecommunications Masterplan includes several references to universal service and the USF. Key connectivity targets for 2020 are as follows:
1) Over 90% of Myanmar population covered by a telecommunications network;
2) Over 85% of Myanmar population covered by a network that provides internet access;
3) Over 50% of Myanmar population with access to a high-speed internetconnection.
Telecom Policy and ICT Policy
Telecom Policy
- To increase the deployment of national IT infrastructure
- To provide a financially viable telecommunications sector conducive to sustainable investment in telecommunications
- infrastructure
- To improve the efficiency and effectiveness of telecommunications service delivery to end-users
- To provide telecommunication services at the affordable price
- To fulfil universal services obligation to the people of Myanmar
ICT Policy
- To promote cooperation for ICT development
- To enhance competitiveness of the ICT sectors
- To promote cooperation to reduce digital divide
- To promote cooperation between State and private sectors
- To increase the availability of information technologies to all the citizens of our country
E-Government Master Plan (2016-2020)
- MCIT has started the preparation of Myanmar e-Governance Master Plan with the support of ADB and Infosys Ltd in 2014
- Revised in 2016
- Implement by MOTC with the cooperation of the international Consultants from IDA and KPMG in 2016
Guidelines for the implementation of e-Government
- Intended to extend utility based on existing resources. (e.g., e-Government network will be built on existing fibre network along the
railway and road)
- To ensure that G2G, G2B and G2C services should meet the utility needs of citizens and businesses
Assessment of ICT and e-Government Policies
- Computer Science Development Law (1996)
- Electronic Transaction Law (2004), Amended (2014);
- The Telecommunications law (2013)
Economic Policy for ICT
- One of the National Objectives in August 2016
- To establish
- Data ID Card System,
- Digital Government Strategy and
- e-Government system
DEDC Master Plan – 7 Key Sectors
1.Education and Learning
2.Healthcare and Welfare sector
3.Financial Services sector
4.Agriculture sector
5.Manufacturing sector
6.Tourism, Hospitality and Retail sector
7.Government services
Note: Digital Economy Development Committee (DEDC)
Operator Licensing
LICENSE PROCESSING TIMELINE
| License Type | Applied for or Applied by | Ministry Approval | Union Government Approval | Processing Timeline |
| NFS (I) | Int’l Gateway Or Foreign person | Yes | Yes | 90 days |
| Otherwise | Yes | No | 60 days | |
| NS | Foreign person | Yes | Yes | 90 days |
| Otherwise | Yes | No | 60 days | |
| NFS (C) | Foreign person | Yes | Yes | 60 days |
| Otherwise | Yes | No | 30 days | |
| AS | Foreign person | Yes | Yes | 60 days |
| Otherwise | Yes | No | 30 days |
Technical and Administrative Requirements
TELECOMS REGULATION
The Posts and Telecommunications Department (“Telecommunications Department”) under the Ministry of Transport and Communications (“MOTC”) is the telecommunications regulator in Myanmar.
The responsibilities of the Telecommunications Department include:-
- the issuance and renewal of service provider licences;
- regulation of the frequency spectrum and numbering plans;
- ensuring consumer protection;
- inspection and supervision of service providers;
- initiating administrative actions against service providers.
As part of sector reforms, the MOTC is authorised to establish the following bodies:-
National Telecommunications Advisory Committee
- Make recommendations on technical standards, consumer protection and strategic development of the telecommunications sector in Myanmar,
- To hear administrative appeals against the MOTC’s decisions.
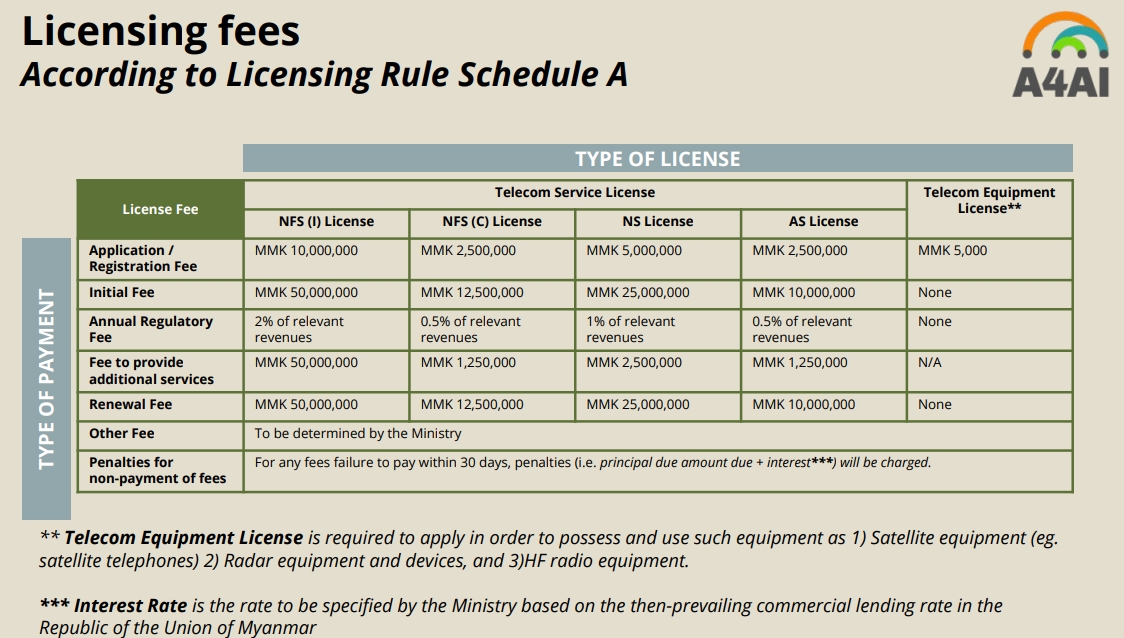
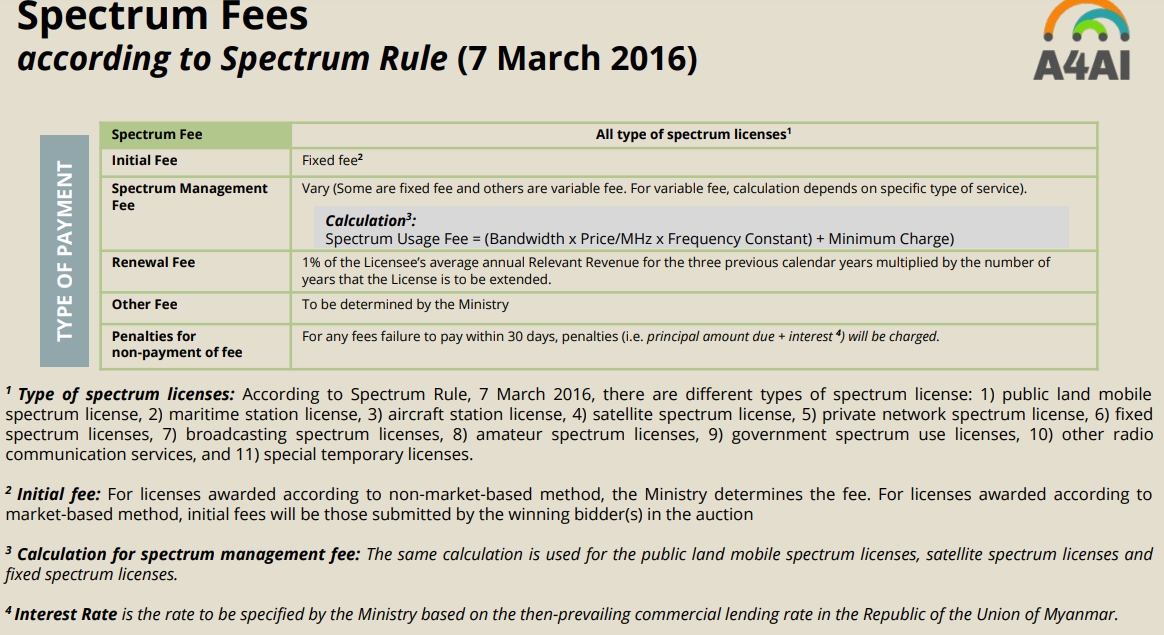
Licensing Fees
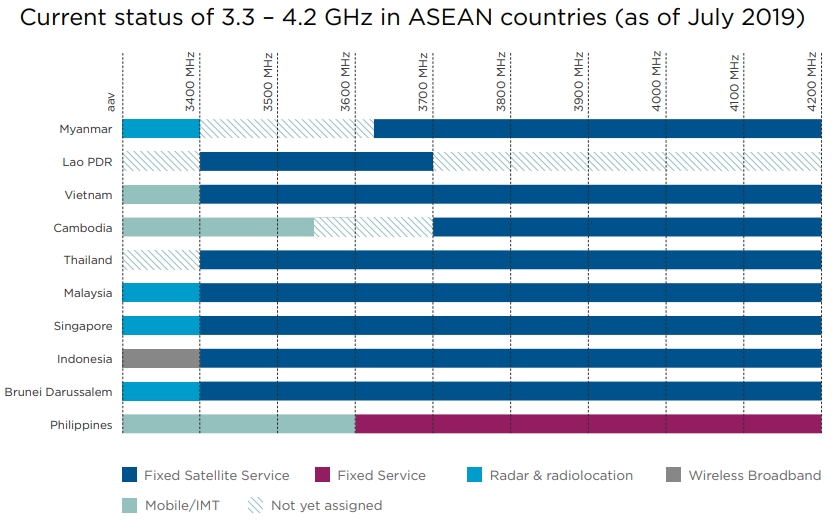
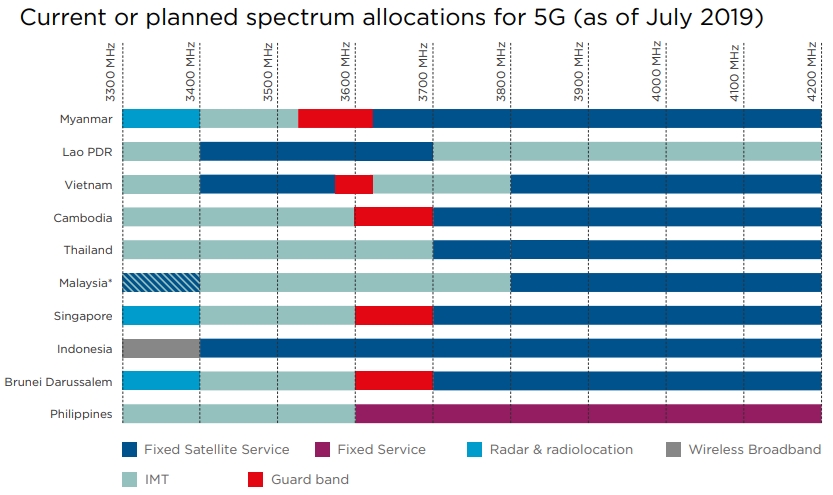
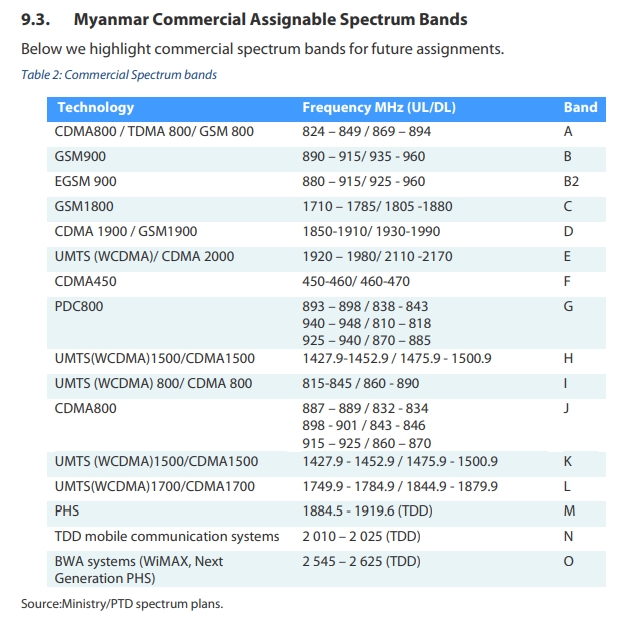
Access to Spectrum
All the guide for application and procedure and fees are here: https://ptd.gov.mm/ServicesDetail.aspx?id=18&__ncforminfo=QFFd0cALmJsGx4tqx5i3TOkiPHsyPePkuzER8TGyqpu5xZ5VSI7bhOPhJZLQpK755_bjivWgt6UL8dMKfC5frA==
Technical and Administrative Requirements
Licensed
Access Networks
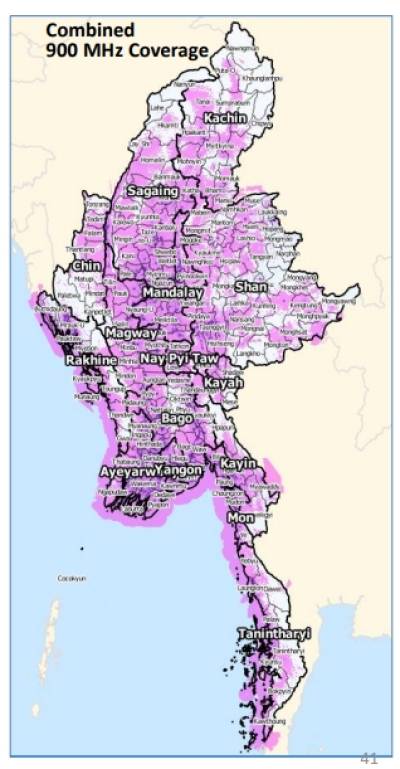
| Operator | 800MHz | 900MHz | 1800MHz | 2100MHz | 2600MHz | 3500MHz |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XYZcom | None | 2×10 | 2×15 | 2×10 | None | None |
PtP Networks
License-Exempt
Access Networks
| Frequency | Power Limit | Transmit Power |
|---|---|---|
| 2.4GHz | ||
| 2400 – 2483.5 MHz | 2.4EIRP |
|
| 5GHz | ||
| 5150-5250 MHz | 5.1EIRP |
|
| 5250-5350 MHz | 5.2EIRP |
|
| 5470-5725 MHz | 5.4EIRP |
|
| 5725-5800 MHz | 5.8EIRP |
|
PtP Networks
| Frequency | Power Limit | Transmit Power |
|---|---|---|
| 2.4GHz | ||
| 2400 – 2483.5 MHz | 2.4EIRP |
|
| 5GHz | ||
| 5150-5250 MHz | 5.1EIRP |
|
| 5250-5350 MHz | 5.2EIRP |
|
| 5470-5725 MHz | 5.4EIRP |
|
| 5725-5800 MHz | 5.8EIRP |
|
Secondary Use
Access Networks
PtP Networks
Spectrum Fees / Costs
Application
All telecom and communication license application process and fees https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Services.aspx
Licensing and Inspection Division
Auction
All of telecommunication related tender call are here https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Announcement.aspx?id=2&__ncforminfo=i7C4b9XQ2ZJHJAaaVLiZ6yAW3y0hQCHR6R7XD9qufUEZ2okGRZ_fCfMeWmhKUBEnt90g8FEfgFyvMCRA1PoUwLdOj-PwoB2t
License holder list https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Uploads/License/Attach/12020/78536142212020_Website%20New%20%20Licence.pdf
Tower list https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Uploads/License/Attach/122019/9655593122019_Co.,Ltd%20Tower%20Update.pdf
List of the optical fiber path https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Uploads/License/Attach/112019/25121419112019_BACKBONE%20FIBER%20UPDATE%20(9-2019)%20.pdf
Microwave Band Plan (31 Jan 2019 Update) https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Uploads/License/Attach/22019/821915622019_Micro%20Band%20Plan%20Update(31.1.2019)English.pdf
Public Land Mobile Spectrum (31 Jan 2019 Update) https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Uploads/License/Attach/22019/1681015622019_Band%20plan%20Update%20(31.1.19)%20English.pdf
List of FM Station and their license https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Uploads/License/Attach/52019/5761315752019_FM%20(Enhlish).pdf
Toll-Free Number list https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Uploads/License/Attach/22019/3428161422019_Allocated%20Tollfree%20Number%20Data.pdf
Mobile numbering list https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Uploads/License/Attach/12020/4517141412020_Allocated%20Mobile%20Number%20Data%20.pdf
Backhaul
Telecommunications Infrastructure (August, 2017)
| Indicator | Statistic / Description |
| Telecom Operator | 4 (2 from domestic, 2 from International) |
| National Fiber Backbone | 549,55.23 Kilometer |
| International Submarine Cable | SEA-ME-WE-3, SEA-ME-WE-5, AAE1 (Ongoing Project) |
| Cross-border Fiber | China – Myanmar, India-Myanmar, Lao-Myanmar, Thailand – Myanmar(4 Links) |
| International Bandwidth | 324.10 Gbps |
| International Gateway | 5 |
| Tower Over | 18,000 towers |
| Number of Telephone | Fixed Phone - 0.52 million, Mobile Phone - 55.61 million, Total - 56.13 million |
| Telephone density | 108.56 % |
| Internet Users | 46.39 Million |
| Internet Penetration | 89.73% |
Gender
Universal Service
What is Universal Service?
* a policy goal to ensure that all people in a country have access and are able to use telecommunications services. * in particular for people living in rural and remote parts of the country and poorer households.
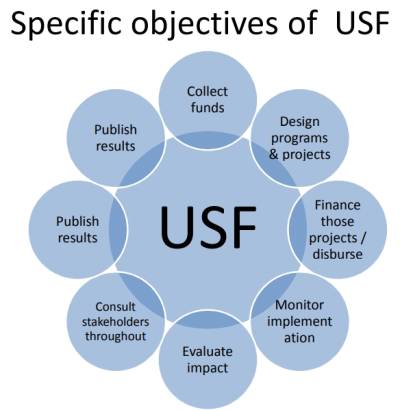
Specific objectives of USF
Collect funds ⇒ Design programs & projects ⇒ Finance those projects / disburse ⇒ Monitor implementation ⇒ Evaluate impact ⇒ Consult stakeholders throughout ⇒ Publish results ⇒ Publish results
Scope of Universal Service
| Issue | Basic meaning | Specification |
| Availability | All inhabitants have service available | Coverage of inhabited geographic territory · Region /area · Locality size (e.g., towns, villages, settlements with varying number of inhabitants) |
| Accessibility | All inhabitants can access the service | Gender · Race, tribe, religion · Ability /disability |
| Affordability | All inhabitants can afford to pay | · Access device (e.g., mobile phone) · Cost of calls & services · Minimum “basket” below a certain national limit (e.g., 3% of family income) |
| Ability | All inhabitants have the telecom services | With increasing focus on the broadband Internet, user capabilities become important · Awareness of services and their benefits · Ability to use computers & devices · Ability to navigate the Internet & use ICT services |
Universal Service Strategy Outcomes
- Increasing & accelerating Voice and Internet broadband provision.
- More people have access to services & applications, as well as the capacity to use them.
- Creating opportunities for both economic & social growth.
Program 1 Infrastructure Roll-out: Voice & Broadband
Voice
- Operators will reach at least 94% by Q1, 2019
- Target: within 5 years 99% of the population to be covered by mobile signal
- Service for an additional 3.2 million people
Broadband Internet
- Target: 95% of the population will have broadband Internet within 5 years
- Total estimated subsidy cost USD 25.4 million
Program 2 ICT Capacity Building: Enabling the Digital Future
Target
- Increase capacity of population to use the Internet for their socio-economic benefit and Myanmar development
- Many links between increased ICT capacity and economic growth and social development
Two Sub-Programs
- Broadband Internet connectivity for various learning & other institutions
- Digital literacy project with eligible local organizations
Program 3 Special Programs
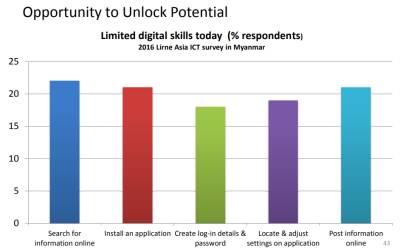
Purpose
- integrate other aspects of universal service which won’t fit in Program 1&2
- Explore new approaches to be used later in mainstream program
Types of Special Projects
- ICT content, service or application for development for rural users/ lower income groups
- Improved access/ usability for persons with disabilities
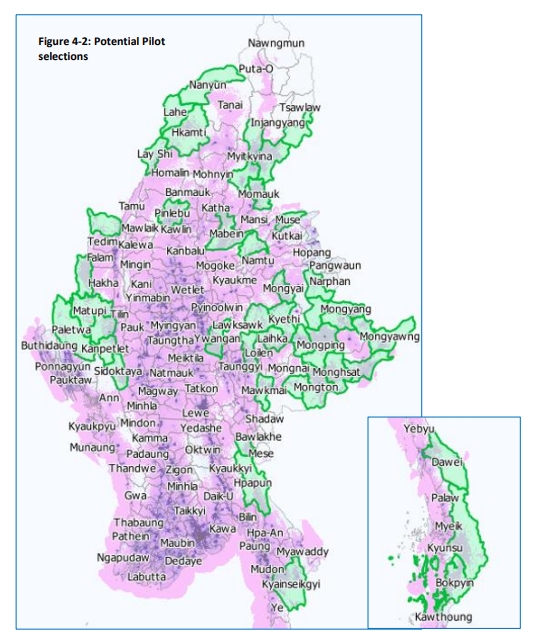
- Small pilot for broadband connectivity (e.g., rural hospitals)
- Any other pilot or research projects
Proposed Pilot
- Funding to translate special software to assist persons with disabilities to use
- ICT – RFP process
USF Progress
- Universal Service Strategy (Final)
- Guideline for USF
- Public Consultation
- Implementing Pilot Project
- Implementing Universal Service Strategy
Laws and Regulations
THE TELECOMS LAW The Telecommunications Law No. 31/2013 (“Telecoms Law”) was introduced on 8 October 2013, providing a modern regulatory framework for Myanmar’s telecommunications sector. The Telecoms Law regulates network facility services, network service providers and application service providers.
THE LICENSING RULES The Telecoms Law is supplemented by Notification No. 16/2014 (Licensing Rules) issued by the then Ministry of Communications and Information Technology of the Union Government (MCIT), which introduced rules and regulations in respect of licensing as well as the implementing regulations to the Telecoms Law. The Telecoms Law and Licensing Rule have been augmented by the following legislation
Note: MCIT reorganized as Ministry of Transport and Communications (MOTC) Notification No. 9/2016 (25 May 2016)
| Legislation | Date |
|---|---|
| Interconnection and Access Rules | 6 January 2015 |
| Telecoms Competition Rules | 9 June 2015 |
| The Numbering Rules | 3 December 2015 |
| The Spectrum Rules | 7 March 2016 |
| Technical Specifications for Short Range Device | 17 July 2016 |
| Guidelines on the Provision of International Gateway Services | 8 September 2016 |
| Telecommunications Numbering Plan | 31 January 2017 |
| The Technical Specification and Quality of Service for International Gateway Service | 5 April 2017 |
| Draft Myanmar Communications Regulatory Commission Law (MCRC Law) | 15 May 2017 |
| The Law Amending the Telecommunication Law | 18 August 2017 |
Other laws and regulations related to Telecom sector in Myanmar
| Year | Law and Regulation |
| October, 1885 | Myanmar Telegraph Act (India Act XIII)1 |
| January, 1934 | Myanmar Wireless Telegraph Act (India Act XVII)2 |
| March, 1989 | State-owned Economic Enterprises Law3 |
| October, 1993 | Amendment of Myanmar Wireless Telegraph Act4 |
| September, 1996 | Computer Science Development Law5 |
| April, 2004 | Electronic Transactions Law6 |
| January, 2011 | Myanmar Special Economic Zone Law7 |
| October, 2013 | Telecommunications Law8 |
| December, 2013 | Licensing rules9, Interconnection and access rules10, Spectrum rules11, Numbering rules12 and Competition rules13 |
Resources / References
1. http://www.mcpt.gov.mm/mcpt/myanmar-telegraph-act.htm
2. http://www.mcpt.gov.mm/mcpt/myanmar-wireless-telegraphy-act.htm
3. http://www.mcpt.gov.mm/mcpt/miscellaneous.htm
4. http://www.mcpt.gov.mm/mcpt/amendment.htm
5. http://www.mcpt.gov.mm/mcpt/myanmar-computer-science-development-law.htm
6. http://unpan1.un.org/intradoc/groups/public/documents/un-dpadm/unpan041197.pdf
7. http://www.mcpt.gov.mm/mcpt/miscellaneous.html
8. http://www.mcit.gov.mm/content/telecommunications-law.html
9. https://www.motc.gov.mm/sites/default/files/1%20-%20MCIT%20-%20Final%20Licensing%20Rules%20-%20122013%20CLEAN.pdf
10. https://www.motc.gov.mm/sites/default/files/3%20-%20MCIT%20-%20Annex%20B%20-%20Proposed%20Interconnection%20Rules%20-%2011113.pdf
11. https://www.motc.gov.mm/sites/default/files/3%20-%20MCIT%20-%20Final%20Spectrum%20Rules%20-%20122213%20CLEAN-1.pdf
12. https://www.motc.gov.mm/sites/default/files/4-%20MCIT%20-%20Final%20Numbering%20Rules%20-%20%20122213%20CLEAN-1.pdf
13. https://www.motc.gov.mm/sites/default/files/5%20-%20MCIT%20-%20Final%20Competition%20Rules%20-%20122213%20CLEAN.pdf