This is an old revision of the document!
Myanmar
Brief About Myanmar
The Republic of the Union of Myanmar, commonly shortened to Myanmar.
Geography
- The total land area of 676,577 square kilometre
- International borders of 5858 Kilometer with Bangladesh, India, China, Thailand and Laos
- total coastal line length 2832kilometer
- 2090 kilometre (north to south )and 925 kilometres (east to west )
Topography
- 50% of mountains and forests (northern and eastern)
Population
- Over 51.49 million Population
- 135 ethnic groups
- Seven states and seven Regions
- 70% of the population lived in rural areas and occupied in agriculture sectors
Natural Resources
- Rice, minerals, teak, hardwood forest, onshore and offshore oil fields, and precious stones such as rubies, jade sapphires, and pearls with the highest quality
Telecommunications Sector Reform
Policy Reform
- The Myanmar Telegraph Act 1885, The Myanmar Wireless Telegraph Act 1934 –> Telecommunications Law 2013
- Telecommunication Service License (Chapter III of Telecommunication Law) –> Anyone who is willing to provide telecommunications facilities and/or telecommunication services shall apply for permission and license
Key Objectives of Licensing Regime
- Promote competition and liberalization of the telecom sector in Myanmar
- Ensure transparency in market entrance
- Establish technology-and-service neutral approach to licensing
- Ensure non-discriminatory treatment of similarly situated licensees
Laws and Regulations
| Sr. No | Name | Issued Date |
| 1. | Telecommunication Law | 8-10-2013 |
| 2. | Licensing Rules | 14-10-2014 |
| 3. | Interconnection Rules | 6-1-2015 |
| 4. | Competition Rules | 9-6-2015 |
| 5. | Numbering Rules | 3-12-2015 |
| 6. | Spectrum Rules | 7-3-2015 |
Licensing Framework Multi-service licensing framework ° to simplify licensing
Processes ° encourage entry and expansion of services and ° increase End-User access to Telecommunications Networks and Telecommunications Services.
License Type NFS (I) NS AS NFS (C)
Maximum of two Telecommunications Service Licenses NFS (C) + NS OR AS
Licensing Category
NFS license (not exhaustive)
- Terrestrial fixed-line and radio transmission
- Submarine cable facilities
- Satellite earth station facilities
- Mobile base station facilities and passive infrastructure to deploy networks
NS license (not exhaustive)
- Wireline connectivity services
- Terrestrial wireless connectivity services
- Satellite uplink/downlink connectivity services
- International and domestic network transport and switching services
- International gateway services
AS license (not exhaustive)
- Public payphone services
- Public switched data services
- Audio text hosting services provided on an opt-in basis
- Directory services
- Internet service provider services
- Messaging services and Value-added services
NFS(C) (not exhaustive)
- Towers, masts, ducts
- Trenches and poles
- Dark fibre
Type of License and Licensees
| Sr. | Type of License | Number of Licensees | ||
| 1. | Nationwide Telecommunications License | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| 2. | Network Facilities Service (Individual) License (NFS-I) | 35 | 11 | 46 |
| 3. | Network Facilities Service (Class) License (NFS-C) | 25 | 16 | 41 |
| 4. | Application Service License ( AS ) | 17 | 4 | 21 |
| 5. | Network Service License ( NS) | 9 | 6 | 15 |
| Total | 88 | 39 | 127 |
National Policy
Telecom Policy and ICT Policy
Telecom Policy
- To increase the deployment of national IT infrastructure
- To provide a financially viable telecommunications sector conducive to sustainable investment in telecommunications
- infrastructure
- To improve the efficiency and effectiveness of telecommunications service delivery to end-users
- To provide telecommunication services at the affordable price
- To fulfil universal services obligation to the people of Myanmar
ICT Policy
- To promote cooperation for ICT development
- To enhance competitiveness of the ICT sectors
- To promote cooperation to reduce digital divide
- To promote cooperation between State and private sectors
- To increase the availability of information technologies to all the citizens of our country
Operator Licensing
LICENSE PROCESSING TIMELINE
| License Type | Applied for or Applied by | Ministry Approval | Union Government Approval | Processing Timeline |
| NFS (I) | Int’l Gateway Or Foreign person | Yes | Yes | 90 days |
| Otherwise | Yes | No | 60 days | |
| NS | Foreign person | Yes | Yes | 90 days |
| Otherwise | Yes | No | 60 days | |
| NFS (C) | Foreign person | Yes | Yes | 60 days |
| Otherwise | Yes | No | 30 days | |
| AS | Foreign person | Yes | Yes | 60 days |
| Otherwise | Yes | No | 30 days |
Technical and Administrative Requirements
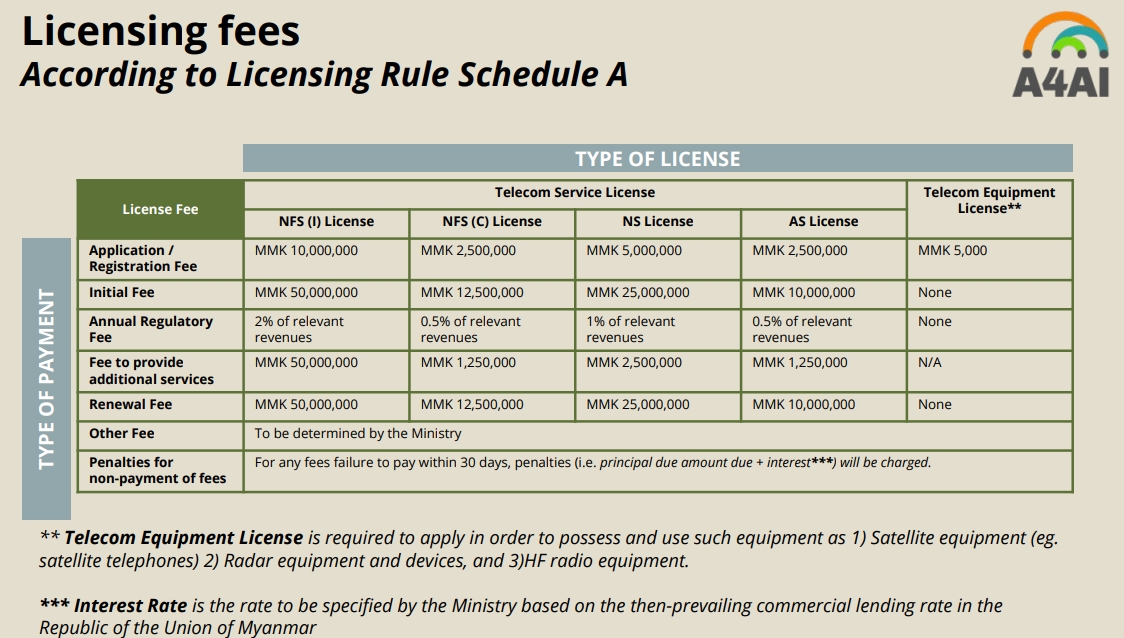
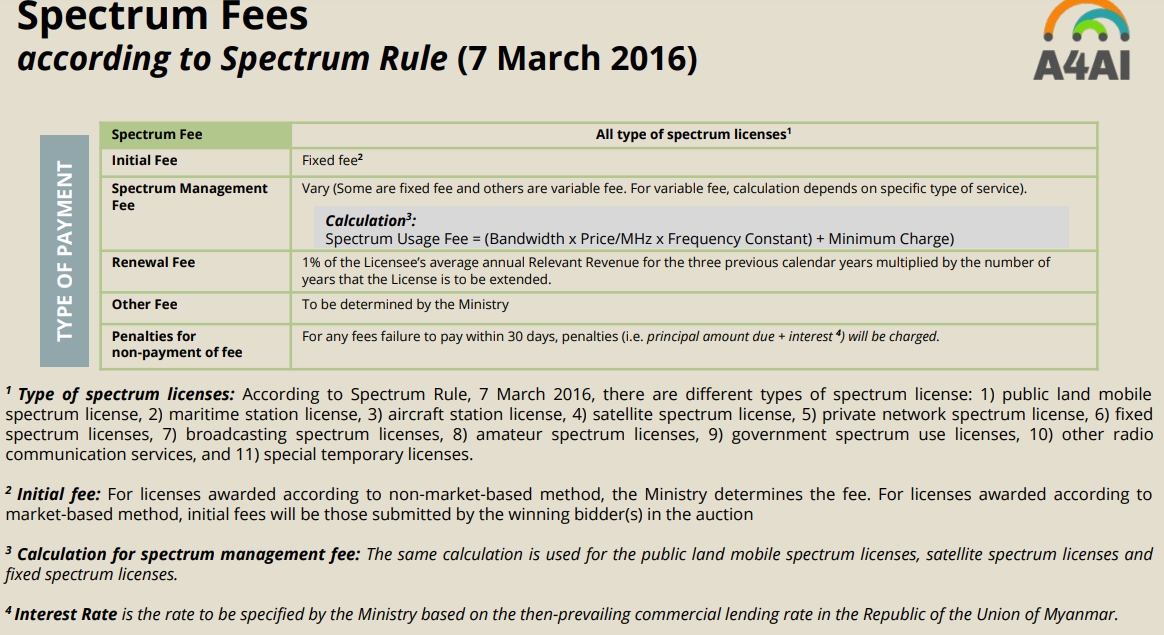
Licensing Fees
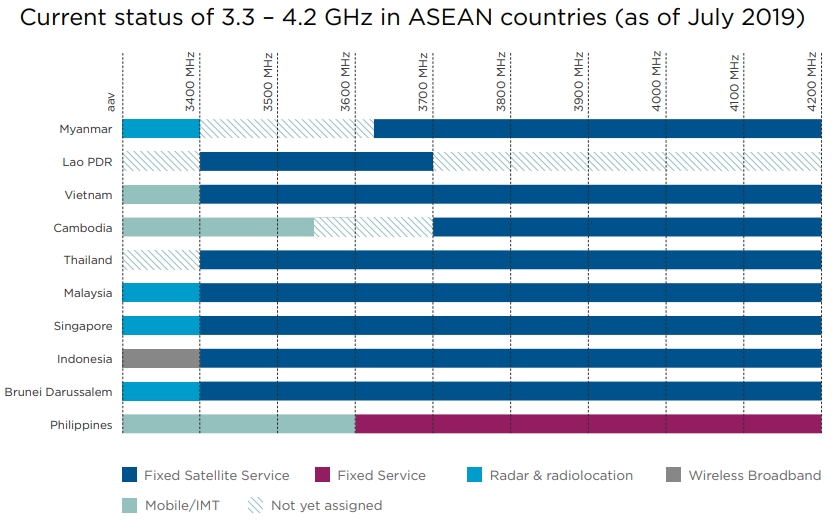
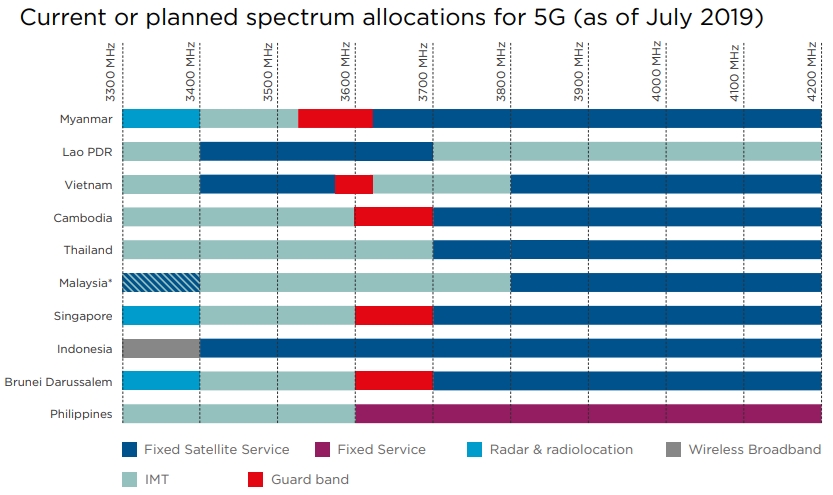
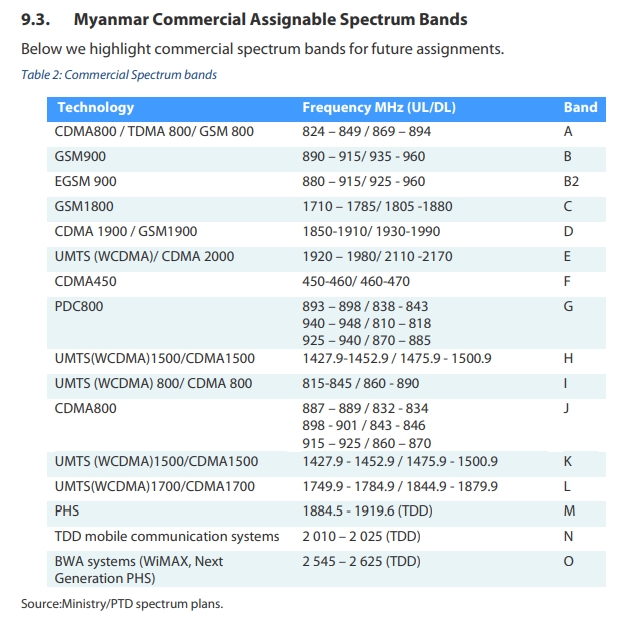
Access to Spectrum
All the guide for application and procedure and fees are here: https://ptd.gov.mm/ServicesDetail.aspx?id=18&__ncforminfo=QFFd0cALmJsGx4tqx5i3TOkiPHsyPePkuzER8TGyqpu5xZ5VSI7bhOPhJZLQpK755_bjivWgt6UL8dMKfC5frA==
Technical and Administrative Requirements
Licensed
Access Networks
| Operator | 800MHz | 900MHz | 1800MHz | 2100MHz | 2600MHz | 3500MHz |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XYZcom | None | 2×10 | 2×15 | 2×10 | None | None |
PtP Networks
License-Exempt
Access Networks
| Frequency | Power Limit | Transmit Power |
|---|---|---|
| 2.4GHz | ||
| 2400 – 2483.5 MHz | 2.4EIRP |
|
| 5GHz | ||
| 5150-5250 MHz | 5.1EIRP |
|
| 5250-5350 MHz | 5.2EIRP |
|
| 5470-5725 MHz | 5.4EIRP |
|
| 5725-5800 MHz | 5.8EIRP |
|
PtP Networks
| Frequency | Power Limit | Transmit Power |
|---|---|---|
| 2.4GHz | ||
| 2400 – 2483.5 MHz | 2.4EIRP |
|
| 5GHz | ||
| 5150-5250 MHz | 5.1EIRP |
|
| 5250-5350 MHz | 5.2EIRP |
|
| 5470-5725 MHz | 5.4EIRP |
|
| 5725-5800 MHz | 5.8EIRP |
|
Secondary Use
Access Networks
PtP Networks
Spectrum Fees / Costs
Application
All telecom and communication license application process and fees https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Services.aspx
Licensing and Inspection Division
Auction
All of telecommunication related tender call are here https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Announcement.aspx?id=2&__ncforminfo=i7C4b9XQ2ZJHJAaaVLiZ6yAW3y0hQCHR6R7XD9qufUEZ2okGRZ_fCfMeWmhKUBEnt90g8FEfgFyvMCRA1PoUwLdOj-PwoB2t
License holder list https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Uploads/License/Attach/12020/78536142212020_Website%20New%20%20Licence.pdf
Tower list https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Uploads/License/Attach/122019/9655593122019_Co.,Ltd%20Tower%20Update.pdf
List of the optical fiber path https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Uploads/License/Attach/112019/25121419112019_BACKBONE%20FIBER%20UPDATE%20(9-2019)%20.pdf
Microwave Band Plan (31 Jan 2019 Update) https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Uploads/License/Attach/22019/821915622019_Micro%20Band%20Plan%20Update(31.1.2019)English.pdf
Public Land Mobile Spectrum (31 Jan 2019 Update) https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Uploads/License/Attach/22019/1681015622019_Band%20plan%20Update%20(31.1.19)%20English.pdf
List of FM Station and their license https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Uploads/License/Attach/52019/5761315752019_FM%20(Enhlish).pdf
Toll-Free Number list https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Uploads/License/Attach/22019/3428161422019_Allocated%20Tollfree%20Number%20Data.pdf
Mobile numbering list https://www.ptd.gov.mm/Uploads/License/Attach/12020/4517141412020_Allocated%20Mobile%20Number%20Data%20.pdf
Backhaul
Telecommunications Infrastructure (August, 2017)
| Indicator | Statistic / Description |
| Telecom Operator | 4 (2 from domestic, 2 from International) |
| National Fiber Backbone | 549,55.23 Kilometer |
| International Submarine Cable | SEA-ME-WE-3, SEA-ME-WE-5, AAE1 (Ongoing Project) |
| Cross-border Fiber | China – Myanmar, India-Myanmar, Lao-Myanmar, Thailand – Myanmar(4 Links) |
| International Bandwidth | 324.10 Gbps |
| International Gateway | 5 |
| Tower Over | 18,000 towers |
| Number of Telephone | Fixed Phone - 0.52 million, Mobile Phone - 55.61 million, Total - 56.13 million |
| Telephone density | 108.56 % |
| Internet Users | 46.39 Million |
| Internet Penetration | 89.73% |
Gender
Universal Service
What is Universal Service?
* a policy goal to ensure that all people in a country have access and are able to use telecommunications services. * in particular for people living in rural and remote parts of the country and poorer households.
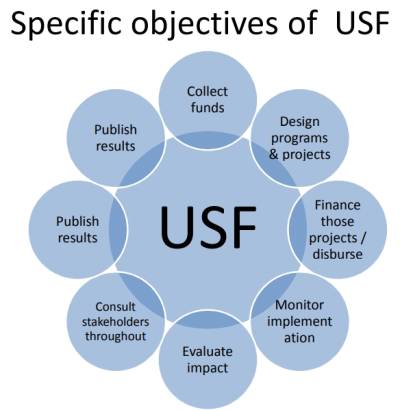
Specific objectives of USF
Collect funds ⇒ Design programs & projects ⇒ Finance those projects / disburse ⇒ Monitor implementation ⇒ Evaluate impact ⇒ Consult stakeholders throughout ⇒ Publish results ⇒ Publish results
Scope of Universal Service
| Issue | Basic meaning | Specification |
| Availability | All inhabitants have service available | Coverage of inhabited geographic territory · Region /area · Locality size (e.g., towns, villages, settlements with varying number of inhabitants) |
| Accessibility | All inhabitants can access the service | Gender · Race, tribe, religion · Ability /disability |
| Affordability | All inhabitants can afford to pay | · Access device (e.g., mobile phone) · Cost of calls & services · Minimum “basket” below a certain national limit (e.g., 3% of family income) |
| Ability | All inhabitants have the telecom services | With increasing focus on the broadband Internet, user capabilities become important · Awareness of services and their benefits · Ability to use computers & devices · Ability to navigate the Internet & use ICT services |
Universal Service Strategy Outcomes
- Increasing & accelerating Voice and Internet broadband provision.
- More people have access to services & applications, as well as the capacity to use them.
- Creating opportunities for both economic & social growth.
Program 1 Infrastructure Roll-out: Voice & Broadband
Voice
- Operators will reach at least 94% by Q1, 2019
- Target: within 5 years 99% of the population to be covered by mobile signal
- Service for an additional 3.2 million people
Broadband Internet
- Target: 95% of the population will have broadband Internet within 5 years
- Total estimated subsidy cost USD 25.4 million
Program 2 ICT Capacity Building: Enabling the Digital Future
Target
- Increase capacity of population to use the Internet for their socio-economic benefit and Myanmar development
- Many links between increased ICT capacity and economic growth and social development
Two Sub-Programs
- Broadband Internet connectivity for various learning & other institutions
- Digital literacy project with eligible local organizations
Program 3 Special Programs
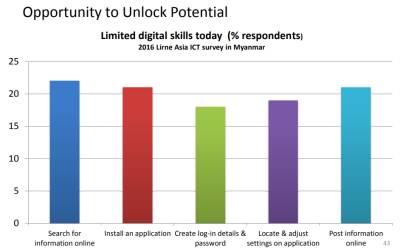
Purpose
- integrate other aspects of universal service which won’t fit in Program 1&2
- Explore new approaches to be used later in mainstream program
Types of Special Projects
- ICT content, service or application for development for rural users/ lower income groups
- Improved access/ usability for persons with disabilities
- Small pilot for broadband connectivity (e.g., rural hospitals)
- Any other pilot or research projects
Proposed Pilot
- Funding to translate special software to assist persons with disabilities to use
- ICT – RFP process
USF Progress
- Universal Service Strategy (Final)
- Guideline for USF
- Public Consultation
- Implementing Pilot Project
- Implementing Universal Service Strategy
Laws and Regulations
| Year | Law and Regulation |
| October, 1885 | Myanmar Telegraph Act (India Act XIII)1 |
| January, 1934 | Myanmar Wireless Telegraph Act (India Act XVII)2 |
| March, 1989 | State-owned Economic Enterprises Law3 |
| October, 1993 | Amendment of Myanmar Wireless Telegraph Act4 |
| September, 1996 | Computer Science Development Law5 |
| April, 2004 | Electronic Transactions Law6 |
| January, 2011 | Myanmar Special Economic Zone Law7 |
| October, 2013 | Telecommunications Law8 |
| December, 2013 |